mapToInt, mapToDouble, mapToLong
Stream API의 map은 반환하는 형태에 따라 여러 메서드가 존재
중간 연산
mapToInt().sum() 총합
만약 double 자료의 총합을 구해야 할 때는 mapToDouble.sum()
// 메뉴 목록에 있는 요리들의 총 칼로리 수 구하기
int sum = menuList.stream()
.mapToInt(d -> d.getCalories())
.sum();
System.out.println("sum = " + sum); // 4300
mapToInt().average().getAsDouble() 평균
average()는 OptionalDouble을 리턴하기 때문에 getAsDouble 필요
// 육류 메뉴의 평균 칼로기
double averageMeatCal = menuList.stream()
.filter(d -> d.getType() == Dish.Type.MEAT)
.mapToInt(d -> d.getCalories())
.average()
.getAsDouble();
System.out.println("averageMeatCal = " + averageMeatCal); // averageMeatCal = 633.3333333333334
anyMatch()
// 메뉴 목록에서 칼로리가 100 이하인 요리가 하나라도 존재하나?
boolean flag2 = menuList.stream()
.anyMatch(d -> d.getCalories() <= 100);
System.out.println("flag2 = " + flag2); //false
allMatch, noneMatch
allMatch: 리스트 안에 모든 객체를 검사해서 모두 일치하는지 확인
noneMatch: 모두 불일치 하는지 검사
// 메뉴 목록의 모든 요리가 1000칼로리 미만입니까?
// allMatch: 리스트 안에 모든 객체를 검사해서 모두 일치하는지 확인
// noneMatch: 모두 불일치 하는지 검사
boolean flag3 = menuList.stream()
.allMatch(d -> d.getCalories() < 1000);
System.out.println("flag3 = " + flag3); // true
정렬
- 정수 배열은 값만 비교하면 됨
- 문자열도 문자값 비교해서 자리바꾸기 하면 됨
- 그러나 객체 안의 숫자는 한 번 더 기준이 필요함
ex. 학생 정렬하면 뭘 기준으로 할건지 ( 학번, 생일, 성적 등… )
sorted
.sorted() 매개변수로 올 수 있는 경우를 확인해보면
파라미터가 없거나 Comparator를 대입할 수 있음
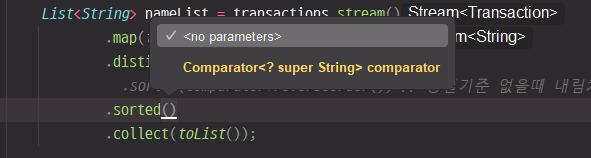
.sorted()
: 정렬 기준이 없을 때 오름차
.sorted(Comparator.reverseOrder())
: 정렬 기준이 없을 때 내림차
interface Comparator
API를 확인해 보면 Comparator는 람다를 사용할 수 있음
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Comparator<T> { ... }
Comprator.comparing(기준)
정렬 기준으로 점수를 사용하기 위해 getScore로 객체에서 점수를 가져옴
내림차순으로
// 성적 순으로 내림차 정렬 (성적 높은 순)
// 오름차
studentList.sort(Comparator.comparing(s -> s.getScore()));
// 내림차
studentList.sort(Comparator.comparing((Student s) -> s.getScore()).reversed());
stream + sorted
// 육류 요리 중 칼로리가 낮은 순으로 정렬
List<Dish> lowCalMeatDishList = Menu.menuList.stream()
.filter(d -> d.getType() == Dish.Type.MEAT)
.sorted(Comparator.comparing(md -> md.getCalories()))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println("lowCalMeatDishList = " + lowCalMeatDishList);
// 칼로리가 300칼로리보다 큰 요리 중
// 칼로리 낮은 순으로 앞에서 3개만 필터링
List<Dish> dishLow3List = menuList.stream()
.filter(d -> d.getCalories() > 300)
.sorted(Comparator.comparing(Dish::getCalories))
.limit(3)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println("dishLow3List = " + dishLow3List);
Collectors.toSet()
Set<String> trCityList = transactions.stream()
.map(t -> t.getTrader().getCity())
// .distinct()
.collect(toSet());
System.out.println("trCityList = " + trCityList);
** 성능을 위해 데이터를 최대한 줄이고 정렬하는 것을 권장
filter, distinct → map → sorted
.stream().max(Comparator.comparing(기준))
int를 OptionalInt 타입을 반환
OptionalInt의 value에 int 값이 있고 getAsInt 메서드명으로 가져올 수 있음 (OrElse…)
// 모든 거래에서 최고거래액은 얼마인가?
int max = transactions.stream()
.mapToInt(Transaction::getValue)
.max().getAsInt();
System.out.println("max = " + max);
.stream().min(Comparator.comparing(기준))
기준의 최소값 가진 객체를 추출
Booking cheapestBooking = bookings.stream()
.min(comparing(Booking::getPrice))
.orElse(null);
System.out.println("Cheapest booking: " + cheapestBooking);
Optional
자바의 단점은 널체크 문법이 없어서 NullPointerException이 자주 발생함
이를 방지하기 위해 Optional로 일단 감싸서 null에 대한 처리를 지정할 수 있음
Transaction min2 = transactions.get(0);
if(min2 != null) {
//blahblah
}
Transaction min3 = transactions.stream()
.min(comparing(Transaction::getValue))
.orElse(null); // 만약 결과가 null일 경우 null 내보냄
그룹화 Map<K, List<L>>
방법 1. 연도별로 filter 후 각각 Map에 추가
Map<Integer, List<Transaction>> groupByYearMap = new HashMap<>();
List<Transaction> trs2021 = transactions.stream()
.filter(t -> t.getYear() == 2021)
.collect(toList());
List<Transaction> trs2022 = transactions.stream()
.filter(t -> t.getYear() == 2022)
.collect(toList());
groupByYearMap.put(2021, trs2021);
groupByYearMap.put(2021, trs2022);
for (Integer year: groupByYearMap.keySet()) {
System.out.println("year: " + year);
for (Transaction tr : groupByYearMap.get(year)) {
System.out.println(tr);
}
}
방법2. groupingBy 사용
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(키))
groupingBy(연도) → 연도가 key가 되고 매칭되는 객체를 리스트로 묶어줌
Map<Integer, List<Transaction>> cambridgeTrsMap = transactions.stream()
.filter(trs -> trs.getTrader().getCity().equals("Cambridge"))
.collect(groupingBy(trs -> trs.getYear()));
// Map 요소 출력
cambridgeTrsMap.forEach((key, value) -> {
System.out.println("year = " + key);
value.forEach(System.out::println);
});
** .equalsIgnoreCase(”비교문자”)
- 대소문자 상관없이 문자열 비교
- 보통 문자열 비교 시 모두 소문자로 바꾼 후 비교
람다 정리
- 메서드 참조
(args) -> ClassName.staticMethod(args) => ClassName::staticMethod
(args0, rest) -> args0.instanceMethod(rest) => ClassName::instanceMethod
(args) -> expr.instanceMethod(args) => expr::instanceMethod
- 생성자 참조
() -> new Constructor() => ClassName::new
(args) -> new Constructor(args) => ClassName::new
List<SimpleDish> simpleDishList = menuList
.stream()
// .map(dish -> new SimpleDish(dish.getName(), dish.getCalories()))
// .map(dish -> new SimpleDish(dish))
.map(SimpleDish::new)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// simpleDishList.forEach(simpleDish -> System.out.println(simpleDish));
simpleDishList.forEach(System.out::println);

